Human rights (as in the UN – Universal Declaration of Human Rights) are fundamental rights and freedoms inherent to all individuals, regardless of nationality, sex, national or ethnic origin, race, religion, language, or any other status. These rights are universally recognized and protected, aiming to ensure that everyone can live with dignity, freedom, equality, justice, and peace.
Key Aspects of Human Rights
- Universality and Inalienability
- Human rights are universal, applying to everyone without exception, and cannot be taken away.
- Indivisibility and Interdependence
- All human rights are indivisible and interdependent, meaning civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights are equally important and interrelated.
- Equality and Non-Discrimination
- Every individual is entitled to their rights without discrimination of any kind.
- Participation and Inclusion
- Every person has the right to participate in political, economic, social, and cultural life.
- Accountability and Rule of Law
- States and other duty-bearers are accountable for the observance of human rights, and there must be legal frameworks to enforce these rights.
Major Categories Of Human Rights
- Civil and Political Rights
- Right to Life and Liberty: Protection against arbitrary deprivation of life and liberty.
- Freedom of Expression: The right to express opinions without censorship or restraint.
- Right to a Fair Trial: Access to a fair and public hearing by an impartial tribunal.
- Freedom from Torture: Protection against torture and cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment.
- Right to Privacy: Protection against arbitrary interference with privacy, family, home, or correspondence.
- Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights
- Right to Work: The right to gain a living by work freely chosen or accepted.
- Right to Education: Access to free and compulsory primary education, and higher education accessible to all.
- Right to Health: The highest attainable standard of physical and mental health.
- Right to an Adequate Standard of Living: Access to adequate food, clothing, housing, and continuous improvement of living conditions.
- Cultural Rights: The right to participate in cultural life, enjoy the benefits of scientific progress, and benefit from the protection of one’s cultural and intellectual property.
- Collective Rights
- Right to Self-Determination: Peoples’ right to determine their political status and pursue their economic, social, and cultural development.
- Right to Development: The right to participate in, contribute to, and enjoy economic, social, cultural, and political development.
- Rights of Indigenous Peoples: Special protection for the rights, cultures, and territories of indigenous peoples.
International Human Rights Framework
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) – 1948
- A foundational document that sets out fundamental human rights to be universally protected.
- International Covenants
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR): Protects civil and political rights.
- International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights (ICESCR): Protects economic, social, and cultural rights.
- Regional Human Rights Instruments
- European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR): Protects human rights in Europe.
- American Convention on Human Rights: Protects human rights in the Americas.
- African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights: Protects human rights in Africa.
- United Nations Human Rights Council
- An inter-governmental body responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights globally.
Challenges and issues in Human Rights
- Violations and Abuses
- Persistent human rights abuses such as genocide, war crimes, torture, and arbitrary detention.
- Inequality and Discrimination
- Ongoing issues of discrimination based on race, gender, sexual orientation, and other statuses.
- Access to Justice
- Barriers to accessing justice for victims of human rights violations.
- Economic and Social Inequalities
- Disparities in economic and social conditions that affect the realization of human rights.
- Freedom of Expression and Privacy
- Threats to freedom of expression and privacy in the digital age, including censorship and surveillance.
Promoting And Protecting Human Rights
- Education and Awareness
- Raising awareness and educating people about their rights and how to protect them.
- Advocacy and Activism
- Supporting human rights organizations and activists in their efforts to promote and defend human rights.
- Policy and Legal Reforms
- Implementing and enforcing laws and policies that protect human rights.
- International Cooperation
- Engaging in international cooperation and solidarity to address global human rights challenges.
- Supporting Vulnerable Groups
- Providing special protection and support to vulnerable groups, including refugees, minorities, and marginalized communities.
Human rights are fundamental to the dignity and well-being of every individual and are crucial for the development of free and just societies. Protecting and promoting these rights is a shared responsibility that requires ongoing commitment and action from individuals, communities, governments, and international organizations.
Diversity
Diversity refers to the presence of differences within a given setting, encompassing various dimensions such as race, ethnicity, gender, age, socioeconomic status, physical abilities, sexual orientation, religious beliefs, political beliefs, and other attributes. Embracing diversity is essential for fostering inclusive environments, driving innovation, and promoting social justice. Here’s an overview of key aspects related to diversity:
Key Aspects of Diversity
Dimensions Of Diversity
- Race and Ethnicity
- Encompasses a variety of cultural backgrounds, languages, and traditions.
- Recognizing and valuing racial and ethnic diversity can reduce discrimination and promote equity.
- Gender
- Includes understanding and respecting the spectrum of gender identities and expressions.
- Promoting gender diversity involves addressing gender biases and ensuring equal opportunities.
- Age
- Acknowledges the value of diverse age groups in contributing different perspectives and experiences.
- Combating ageism and fostering intergenerational collaboration are essential.
- Socioeconomic Status
- Recognizes differences in income, education, occupation, and social class.
- Promoting socioeconomic diversity can address inequality and create opportunities for all.
- Physical and Cognitive Abilities
- Includes people with disabilities and varying physical and mental health conditions.
- Ensuring accessibility and accommodations is crucial for full participation.
- Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
- Embraces the diversity of sexual orientations and gender identities.
- Creating inclusive environments involves supporting LGBTQ+ rights and addressing discrimination.
- Religious and Spiritual Beliefs
- Encompasses a variety of faiths and spiritual practices.
- Respecting religious diversity promotes understanding and tolerance.
- Cultural Background
- Includes traditions, customs, and values from different cultures.
- Valuing cultural diversity enhances global awareness and mutual respect.
Importance Of Diversity
- Innovation and Creativity
- Diverse teams bring multiple perspectives, leading to more innovative solutions and creative ideas.
- Better Decision-Making
- Diversity encourages a broader range of viewpoints, resulting in more informed and effective decisions.
- Enhanced Performance
- Inclusive organizations often perform better financially and operationally.
- Social Cohesion
- Promoting diversity fosters a more inclusive and harmonious society.
- Personal Growth
- Exposure to diverse perspectives broadens individual horizons and enhances personal development.
Challenges And Barriers
- Implicit Bias
- Unconscious biases can influence behavior and decision-making, perpetuating inequality.
- Discrimination and Prejudice
- Persistent discrimination and prejudice can marginalize diverse groups and limit opportunities.
- Stereotypes
- Stereotyping individuals based on group membership can lead to misconceptions and unfair treatment.
- Lack of Representation
- Underrepresentation of certain groups in leadership positions and influential roles can perpetuate disparities.
- Resistance to Change
- Organizational and societal resistance to diversity initiatives can hinder progress.
Strategies For Promoting Diversity
- Education and Training
- Implementing diversity training programs to raise awareness and reduce biases.
- Inclusive Policies and Practices
- Developing policies that promote equity and inclusion, such as diverse hiring practices and equitable pay.
- Representation and Leadership
- Ensuring diverse representation in leadership roles and decision-making processes.
- Mentorship and Support
- Providing mentorship and support networks for underrepresented groups.
- Community Engagement
- Engaging with diverse communities to understand their needs and perspectives.
Global And Organizational Initiatives
- Affirmative Action
- Policies aimed at increasing the representation of historically marginalized groups.
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Programs
- Corporate and institutional programs focused on fostering diverse and inclusive environments.
- International Agreements and Policies
- Various international frameworks and agreements promote diversity and human rights globally.
Embracing diversity is a multifaceted and ongoing effort that requires commitment, empathy, and proactive measures to create environments where everyone can thrive.
Diversity in the context of gender equality and sexual orientation refers to recognizing, valuing, and respecting differences in gender identities, expressions, and sexual orientations.
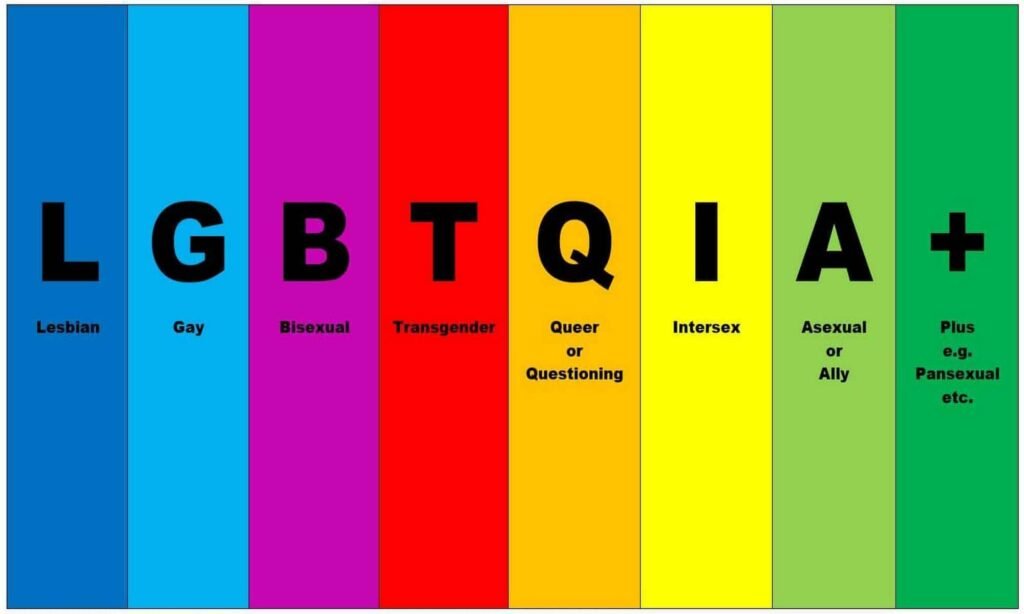
This includes understanding the unique experiences and challenges faced by individuals across the gender spectrum and those who identify as LGBTQ+ (Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer/Questioning, and others). Promoting gender equality and acceptance of diverse sexual orientations is crucial for fostering inclusive, equitable, and just societies.
Gender Equality
Gender equality means ensuring that people of all genders have equal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities. It involves eliminating discrimination and biases based on gender and creating conditions where all individuals can achieve their full potential.
Key Aspects of Gender Equality
- Equal Opportunities
- Ensuring that people of all genders have access to the same opportunities in education, employment, and political participation.
- Pay Equity
- Addressing the gender pay gap by ensuring equal pay for equal work and valuing work typically performed by women.
- Representation
- Increasing the representation of women and gender-diverse individuals in leadership roles and decision-making positions.
- Work-Life Balance
- Promoting policies that support work-life balance, such as parental leave, flexible working hours, and affordable childcare.
- Health and Safety
- Addressing gender-specific health needs and ensuring protection from gender-based violence and harassment.
Sexual Orientation
Sexual orientation refers to an individual’s emotional, romantic, or sexual attraction to others. This includes, but is not limited to, heterosexuality, homosexuality, bisexuality, and asexuality. Acceptance and support of diverse sexual orientations are fundamental to creating inclusive communities where everyone can thrive without fear of discrimination or prejudice.
Key Aspects of Inclusivity for Sexual Orientation
- Legal Protections
- Enacting and enforcing laws that protect individuals from discrimination based on sexual orientation in employment, housing, healthcare, and public services.
- Marriage and Family Rights
- Ensuring equal rights for same-sex couples, including the right to marry and adopt children.
- Representation and Visibility
- Increasing the visibility and representation of LGBTQ+ individuals in media, politics, and public life.
- Supportive Environments
- Creating safe spaces and support networks for LGBTQ+ individuals in schools, workplaces, and communities.
- Healthcare Access
- Providing inclusive and competent healthcare services that address the specific needs of LGBTQ+ individuals.
Intersectionality
Intersectionality is the concept that various forms of social stratification, such as race, gender, sexual orientation, and class, intersect to create unique dynamics and effects. Recognizing intersectionality is crucial for understanding the compounded discrimination faced by individuals who belong to multiple marginalized groups.
Strategies, Efforts, Progress
Promoting diversity, gender equality, and acceptance of diverse sexual orientations is an ongoing effort that requires commitment from individuals, organizations, and governments to create a more equitable and inclusive world.
Promotion strategies
- Education and Awareness
- Implementing education programs that raise awareness about gender diversity, sexual orientation, and the importance of inclusivity.
- Policy Development
- Developing and enforcing policies that promote gender equality and protect against discrimination based on sexual orientation.
- Training and Development
- Providing diversity training for employees, educators, and community leaders to foster inclusive environments.
- Advocacy and Activism
- Supporting advocacy groups and movements that fight for gender equality and LGBTQ+ rights.
- Research and Data Collection
- Conducting research to understand the experiences and challenges faced by diverse gender identities and sexual orientations, informing evidence-based policy decisions.
Global efforts and progress
- United Nations Initiatives
- The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) include goals for gender equality (Goal 5) and reducing inequalities (Goal 10), which encompass sexual orientation and gender identity.
- Legal Reforms
- Many countries have made significant progress in enacting laws that promote gender equality and protect LGBTQ+ rights, although challenges remain.
- Corporate Responsibility
- Increasingly, corporations are adopting diversity and inclusion policies, recognizing that diverse workforces drive innovation and better business outcomes.
What’s More

My Blog (61)
Dependence (5) Fiction (7) Karma (6) Landmarks (4) Paramount (6) Poignancy (5) Spectrum (6) Spotlight (6) Take Off (5) Unique (5) Virtue (6)
Amazing Stuff (9) Beyond Known (8) Controversial (9) Digital World (9) Inequities (8) Innovative (8) Metaphysics (8) Our Society (9) Outer Space (8) Value Creation (9) Yearnings (8)