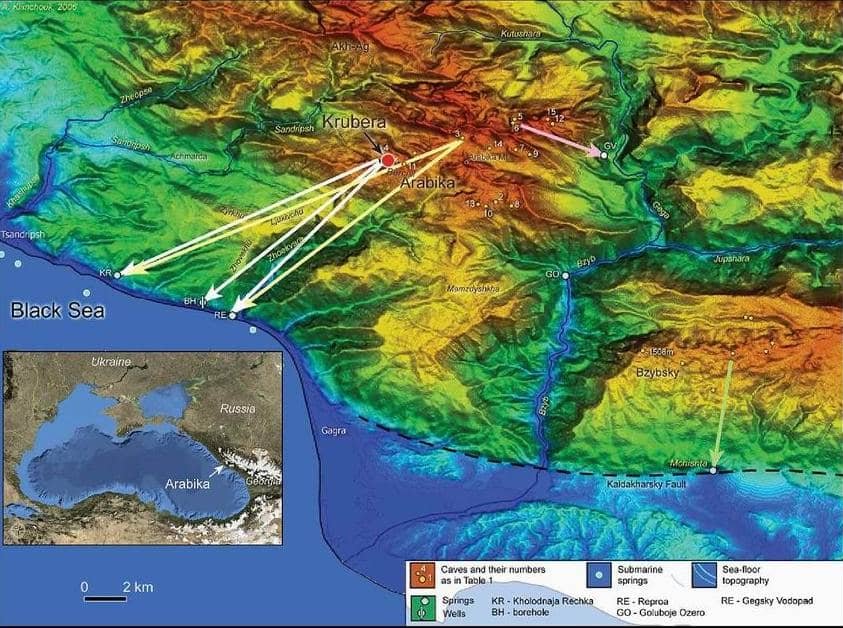
The Krubera Cave

Krubera Cave, located in the Arabika Massif of the stunning Caucasus Mountains in Georgia, holds the title of the deepest cave on Earth (List of Deepest Caves). This natural wonder has captivated explorers and geologists alike due to its remarkable depth, which exceeds 2,197 meters. The cave gained international recognition after its discovery in 1960, igniting a passion for cave exploration and leading to numerous expeditions aimed at uncovering its secrets.
Krubera Cave, the only known cave reaching such profound depths, holds immense scientific significance. Its intricate network of passages showcases unique geological structures formed over millions of years, featuring stunning stalactites and stalagmites. The cave’s complexity presents physical and environmental challenges during exploration.
Numerous expeditions have mapped extensive sections of Krubera Cave, greatly contributing to our understanding of subterranean ecosystems and climatic conditions. Researchers use advanced techniques to measure and chart the cave’s depths while preserving its delicate ecosystem. These efforts have unveiled remarkable geological formations and biological discoveries, highlighting the importance of continued exploration.
Krubera Cave’s allure extends to the scientific community, offering research opportunities into karst topography and organisms in extreme conditions. Continuous studies reveal new insights into subterranean ecosystems, pushing the boundaries of human exploration and scientific understanding. The cave continues to be a focal point for pioneering research and discovery, highlighting the endless curiosity and dedication of those who seek to uncover the Earth’s hidden depths.
Geology and Formation of the Cave

The profound depths of Krubera Cave, recognized as the deepest cave on Earth, can be attributed to its unique geological composition. Formed primarily in limestone, Krubera Cave is a striking example of karst topography, characterized by the dissolution of soluble rocks, leading to the development of dramatic and intricate cave systems. This geological process plays a pivotal role in shaping not only the cave itself but also the surrounding landscape, as water seeps into the ground, gradually eroding the rock to create expansive chambers and corridors.
Water erosion is particularly significant in the formation of Krubera Cave. Over millions of years, acidic rainwater filters through the soil, where it gathers organic acids, which increases its ability to dissolve limestone. This continuous process has led to the excavation of the cave’s extensive passages, resulting in unique geological formations such as stalactites and stalagmites, which are often found in limestone caves. The intricate formations within Krubera are not only aesthetically important but also serve as indicators of the cave’s geological history and the various climatic conditions that prevailed over time.
In terms of geological age, Krubera Cave is estimated to be several million years old, making it a relatively young geological feature compared to some other notable caves worldwide. Its age contributes to its complex structure, consisting of a network of vertical shafts, deep pits, and vast chambers, which are still being explored by researchers and cavers alike.
When compared to other prominent limestone caves, such as Mammoth Cave in the United States, Krubera Cave offers a unique window into geological processes at work, revealing how variables like elevation and geological activity influence cave development. Understanding the geology of Krubera Cave not only enriches our knowledge of this remarkable natural wonder but also highlights the intricate relationship between water, rock, and time in the formation of subterranean landscapes.
Biodiversity Within Krubera Cave
Krubera Cave, renowned as the deepest cave on Earth, hosts a fascinating array of biodiversity that has captured the attention of researchers and biologists worldwide. This subterranean realm is characterized by a unique ecosystem, where a variety of species of flora and fauna thrive in complete darkness. The organisms found within Krubera have evolved remarkable adaptations to survive in the extreme conditions present in the cave’s depths.
The ecosystem within Krubera Cave is primarily dominated by microorganisms, which include bacteria and fungi, capable of surviving on minimal nutrients. These microorganisms are essential in decomposing organic matter and contributing to the nutrient cycle unique to the cave environment.
Researchers have observed invertebrates in Krubera Cave that have adapted to the lack of light and harsh conditions. Subterranean crustaceans and insects exhibit reduced pigmentation and enhanced sensory adaptations to navigate their dark habitat. Some species rely on echolocation to communicate and find food. Krubera Cave offers insights into evolution and biodiversity, demonstrating how life adapts to extreme environments over time. Preserving this unique ecosystem is crucial for understanding life on Earth and the resilience of organisms in challenging habitats. Continued research will reveal more about the remarkable organisms thriving in Krubera Cave’s depths.
Adventuring and Research
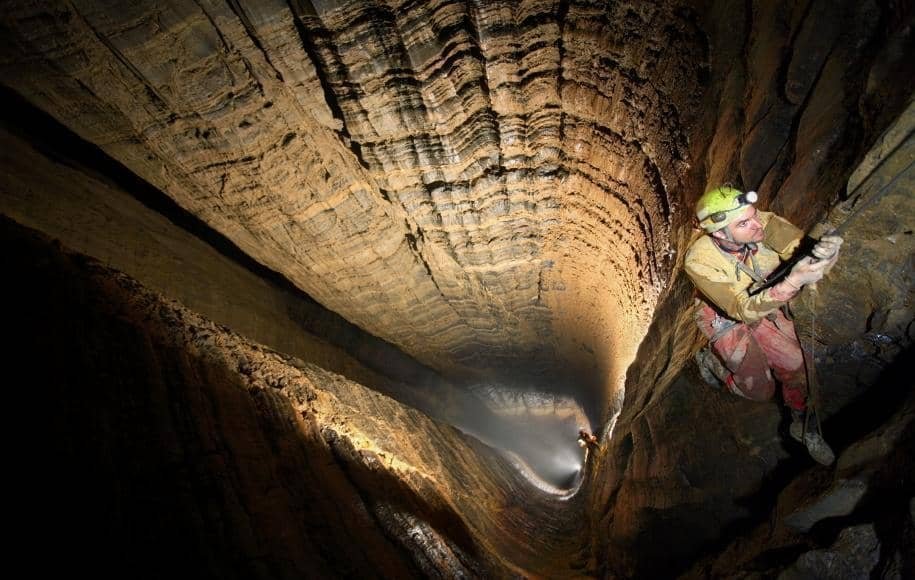

Since Krubera Cave’s discovery, adventurers, spelunkers, and researchers from various countries have explored its labyrinthine passages. Equipped with state-of-the-art gear, they have faced challenges like treacherous vertical drops, submerged chambers, and freezing temperatures.
The equipment necessary for such daring explorations is both specialized and extensive. It often includes advanced climbing gear, various types of ropes, helmets with headlamps, and comprehensive diving equipment for submerged sections of the cave.
Additionally, researchers often carry scientific instruments to assist with data collection, facilitating studies in geology, hydrology, and climate science. The information gathered from explorations of Krubera Cave has shed light on unique underground ecosystems and geological formations that have remained isolated for millennia.
Scientific research within Krubera has provided invaluable insights into hydrology and the impact of climate change on subterranean ecosystems. The ongoing exploration of Krubera Cave is crucial for academic pursuits and conservation. Continuous efforts help protect the delicate balance within the cave, ensuring future generations of explorers and the natural inhabitants of Krubera can thrive. This balance underscores the importance of collaboration among enthusiasts, professionals, and conservationists dedicated to preserving this extraordinary natural wonder.
What’s More
The posts in My Blog feature reflective, story-driven pieces rooted in personal and societal insights.
The topics in My Interests explore abstract, philosophical ideas and their cultural and societal impact.
👁️ 6,563 Views















