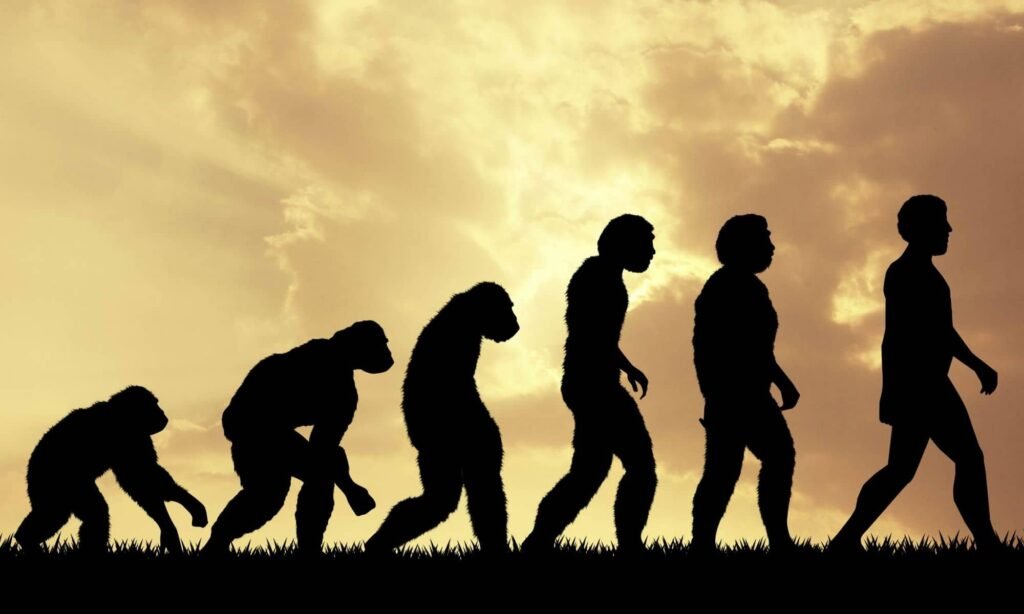
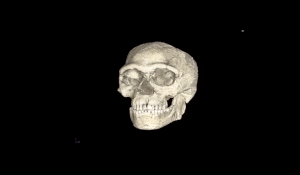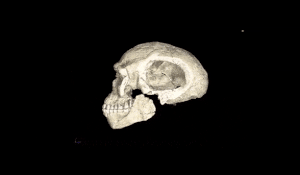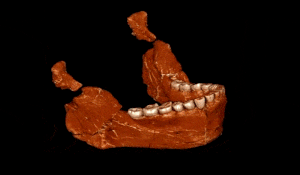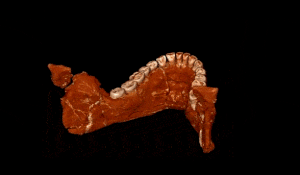
The term “Homo sapiens” translates to “wise man,” highlighting our intelligence. From early beginnings, we developed complex language, technology, and social structures. Our ancestors migrated from Africa, leading to diverse cultures. As we spread, we significantly affected the environment, with the agricultural revolution marking a turning point. Homo sapiens evolved between 200 to 300 thousand years ago in Africa, showcasing remarkable adaptations. Early Homo sapiens were contemporaries of Neanderthals likely descending from Homo Heidelbergensis.
200 to 300 thousand years? Recently discovered bones in a Moroccan mine thought to be up to 350 thousand years old are now believed to represent the earliest known Homo Sapiens fossils.
Perhaps it’s time for a further evolutionary step: Why we’re closer than ever to a Timeline for Human Evolution.
Origins & Materials
Sense & Nonsense
I’m just glad Homo Sapiens has not rested evolving at the stage as shown in Aaaaaaaah!, a 2015 British horror comedy film containing no dialogue, with the cast communicating entirely in animalistic grunts. But then again, if we had evolved like that, we would not have anything else to compare with, would we?
The film Aaaaaaaah! was shot over two weeks during the summer of 2014. The critical reception has been positive, with review aggregator Rotten Tomatoes giving it a rating of 79% based on 14 reviews. The film went on to receive a British Independent Film Awards Nomination, as well as a special jury mention at Cleveland International Film Festival.
Even as Homo Sapiens is today, we take it for granted, normal and consider it a logic outcome that has succeeded previous development stages. But where is it going from here? How much longer could one safely state that Michelangelo’s David, representing the human species, was on the top of the food chain and entitled to behave as if he was the ruler of the universe?
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is a milestone document in the history of human rights. Drafted by representatives with different legal and cultural backgrounds from all regions of the world, the Declaration was proclaimed by the United Nations General Assembly in Paris on 10 December 1948 (General Assembly resolution 217 A) as a common standard of achievements for all peoples and all nations. It sets out, for the first time, fundamental human rights to be universally protected and it has been translated into over 500 languages.
The Future Of Humanity
Dr. Yuval Noah Harari is an Israeli historian and a tenured professor in the Department of History at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem as well as author of international bestsellers.
He explains how revolutions in tech and society will transform our bodies and minds.
Can machines ever have consciousness? Is there an economic value in it? Does organic life any life over inorganic, artificial life? Dr Yuval Noah Harari Answers Questions from the audience following his talk.
Overpopulation
In 2013, Sir David Attenborough said if humans did not control population, the natural world would and in 2018, he stated in an interview with the BBC’s Newsnight, that slowing population growth is key to saving the planet.
By 2025, World Population will probably be over 8 billion people. Around 2040, it could hit 9 billion and by 2100, it could reach a massive 11 billion people.
But don’t panic, there’s a limit says Prof. Hans Rosling
Later In The Universe
“Humans, taxonomically referred to as Homo Sapiens were the galaxy’s most numerous and politically dominant sentient species with millions of major and minor colonies galaxywide.
Believed to have originated on The Earth they could later be found anywhere, engaged in many different pursuits: spacers, mercenaries, smugglers, merchants, soldiers, assassins, farmers, crime lords, laborers, slaves, slavers, and many others.
Since Humans were the most common sentient species, they were often considered to be a standard or average to which the biology, psychology, and culture of other species were compared.”
The intersection of Homo sapiens and the concept of extraterrestrials has long fascinated both the scientific community and the public imagination. Scientific American explores the idea that humans, with our unique genetic makeup and profound impact on the planet, may seem like aliens on a geological timescale. This perspective is echoed by NBC News, which discusses the rarity of terrestrial-style biology and the possibility that Earth might be one of the earliest planets to support life.
The debate on extraterrestrial intelligence questions why we haven’t encountered it yet, highlighting the complexity of life and intelligence in the universe and our quest to understand our place within it. Some theories suggest extraterrestrials may see Homo Sapiens as primitive or uninteresting, avoiding contact. Others propose humans are the real ‘ancient aliens’ due to our unique species and coevolution with the ‘dataome‘ (all the non-genetic data we carry internally and externally – named by analogy data with the genome).
What’s More
The posts in My Blog feature reflective, story-driven pieces rooted in personal and societal insights.
The topics in My Interests explore abstract, philosophical ideas and their cultural and societal impact.
👁️ 6,055 Views


















